MAP AND TYPE I DIABETES MELLITUS (T1DM)
2018-10-31 10:06:43 In 2006 Dr. Tom Dow hypothesized that MAP in cow’s milk could act as a trigger for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) – see the journal Medical Hypotheses 67:782-785, 2006. He now draws together the body of scientific work published since that time, much of it from the laboratory of Dr. Leonardo Sechi, that backs up this highly probable causal association in a short You Tube video related to milk. Watch both and judge for yourself.
In 2006 Dr. Tom Dow hypothesized that MAP in cow’s milk could act as a trigger for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) – see the journal Medical Hypotheses 67:782-785, 2006. He now draws together the body of scientific work published since that time, much of it from the laboratory of Dr. Leonardo Sechi, that backs up this highly probable causal association in a short You Tube video related to milk. Watch both and judge for yourself.
FIRST REPORT OF CHRONIC ENTERITIS IN HUMANS, LATER KNOWN AS CROHN’S DISEASE (1913).
2018-10-25 14:47:08October 25, 2018
 105 years ago today, Thomas Kennedy Dalziel (1861-1924) published the first report of the chronic inflammatory intestinal condition that is now called Crohn’s disease; named for the first of three authors of the 1932 report describing the pathology and clinical presentation of this regional ileitis. Dalziel’s paper describes several cases, three of which have pathology reports. Noteworthy is that Dalziel mentions the gross and microscopic similarities of the intestines he removed from patients with those from cases of Johne’s disease in cattle. He mentions the 1895 work of Johne (misspelled as Henny) and Frothingham and cites the early work on the Johne’s disease pathology by McFadyen. The puzzling aspect is that while the pathology of the human and animal diseases is strikingly similar, acid-fast bacteria (MAP) can be seen in the animal tissues but not in the human tissues: a puzzle that remains today and is the essential feature leading some experts to view the human and animal forms of this chronic enteritis as having different causes.
105 years ago today, Thomas Kennedy Dalziel (1861-1924) published the first report of the chronic inflammatory intestinal condition that is now called Crohn’s disease; named for the first of three authors of the 1932 report describing the pathology and clinical presentation of this regional ileitis. Dalziel’s paper describes several cases, three of which have pathology reports. Noteworthy is that Dalziel mentions the gross and microscopic similarities of the intestines he removed from patients with those from cases of Johne’s disease in cattle. He mentions the 1895 work of Johne (misspelled as Henny) and Frothingham and cites the early work on the Johne’s disease pathology by McFadyen. The puzzling aspect is that while the pathology of the human and animal diseases is strikingly similar, acid-fast bacteria (MAP) can be seen in the animal tissues but not in the human tissues: a puzzle that remains today and is the essential feature leading some experts to view the human and animal forms of this chronic enteritis as having different causes.
Comment: This historically important publication (British Medical Journal vol. 2, no. 2756, pp 1068-1070, October 25, 1913) is made available by JSTOR at the link provided below. Without agencies such as JSTOR it is hard to obtain older literature such as this.
Thomas K. Dalziel was known for his charm, kindliness, extraordinary teaching skills, and marvelous manipulative dexterity. He was considered the best technical surgeon in the West of Scotland. His contributions to the medical literature were considerable, dealing mainly with abdominal surgery. His writings, including this “classic” paper, demonstrate a concise grasp of a new disease entity, chronic interstitial enteritis, later to become known as Crohn's disease. It is generally believed that Dalziel was the first to draw attention to this condition (Diseases of the Colon and Rectum 32:12, pp 1076-1078, 1989).
NEW PHAGE-BASED DIAGNOSTIC TEST COMING TO MARKET.
2018-10-19 13:45:03 At the 2018 meeting of the European Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians (14-17 October, 2018) Pelletier et al. reported on the use of a new phage-based assay called Actiphage™ Rapid kit from PBD Biotech to detect MAP in blood samples from bovine calves. Details are provided in the two page abstract (link below).
At the 2018 meeting of the European Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians (14-17 October, 2018) Pelletier et al. reported on the use of a new phage-based assay called Actiphage™ Rapid kit from PBD Biotech to detect MAP in blood samples from bovine calves. Details are provided in the two page abstract (link below).
Comment: This report is interesting from two perspectives. The first is the biology of MAP infections in dairy calves. This the first report of MAP detection in blood samples of 3 different calves soon after birth; 1, 15, and 84 days of age for the three different calves. The calves reverted to test-negative after the single MAP detection. The second perspective is the promise of improved diagnostics for paratuberculosis using phages to enhance DNA extraction of MAP DNA from clinical samples to enhance the diagnostic sensitivity of real-time PCR assays for MAP.
SURVEY OF MAP INFECTION IN CANADIAN DAIRY HERDS
2018-10-16 15:41:13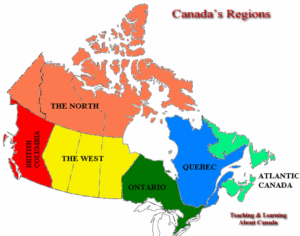 Canadian colleagues at three veterinary schools in Canada teamed up to do the first all-Canada survey to estimate the prevalence of MAP infected dairy herds. The study collected samples from 362 dairy herds in 10 Canadian provinces using environmental fecal cultures as the diagnostic test.
Canadian colleagues at three veterinary schools in Canada teamed up to do the first all-Canada survey to estimate the prevalence of MAP infected dairy herds. The study collected samples from 362 dairy herds in 10 Canadian provinces using environmental fecal cultures as the diagnostic test.
True prevalence estimates were 66% for farms in Western Canada, 54% in Ontario, 24% in Québec, and 47% in Atlantic Canada. Herds housed in tie-stalls had a lower prevalence than freestall-housed herds, and herds with 101–150 and >151 cows had higher prevalence than herds with ≤100 cows. This was the first time MAP prevalence was determined using 1 detection method, performed in 1 laboratory, and within a single year across Canada, enabling direct comparisons of prevalence among regions, housing types, and herd sizes.
This was the first time MAP prevalence was determined using 1 detection method, performed in 1 laboratory, and within a single year across Canada, enabling direct comparisons of prevalence among regions, housing types, and herd sizes. The authors did an elegant job of judging the sensitivity and specificity of their sampling method. Their survey findings are similar those done in Europe and a bit lower than estimates for U.S. dairy herds.
LANDMARK PAPER DEFINING CROHN’S DISEASE (1932)
2018-10-15 15:49:50 Eighty-six years ago today, Burrill B. Crohn, Leon Ginzburg, and Gordon D. Oppenheimer published a paper titled Regional Ileitis – A Pathologic and Clinical Entity in the Journal of the American Medical Association (vol. 99, no. 16, pp 1323-1329, October 15, 1932). Honoring the importance of this report, the article was later reprinted as a Landmark Article in The Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine (vol 67, no. 3, pp 263-268, May 2006). We provide the original JAMA article here for users interested in reading this influential publication in its original form. Note: the reprinted version in the Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine has better print quality. The picture of B.B. Crohn is credited to Wikipedia.
Eighty-six years ago today, Burrill B. Crohn, Leon Ginzburg, and Gordon D. Oppenheimer published a paper titled Regional Ileitis – A Pathologic and Clinical Entity in the Journal of the American Medical Association (vol. 99, no. 16, pp 1323-1329, October 15, 1932). Honoring the importance of this report, the article was later reprinted as a Landmark Article in The Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine (vol 67, no. 3, pp 263-268, May 2006). We provide the original JAMA article here for users interested in reading this influential publication in its original form. Note: the reprinted version in the Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine has better print quality. The picture of B.B. Crohn is credited to Wikipedia.
Comment: I appreciate history as I grow older. Also, it is important to read original published reports to avoid misquoting or perpetuating misunderstandings. Interesting note: As described in Wikipedia, Crohn always preferred the medically descriptive terms "regional ileitis" and "regional enteritis" to "Crohn's disease", but he was not able to prevent the appropriation of his name for the disease.
Without providing much detail, B.B. Crohn’s article mentions efforts to determine if Mycobacterium tuberculosis was involved in the regional ileitis cases he described including culture for M. tuberculosis, inoculation of lymph node homogenates from five patients into guinea pigs, rabbits, and chickens, and acid-fast staining of tissue sections. He concludes that M. tuberculosis was not a cause of these cases of regional ileitis. However, he never mentions the 1913 report by Dalziel or makes any mention of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis or the similarities of regional ileitis in humans to that of cattle, as described by H.A. Johne in 1895. How might history be different had Dr. Crohn mentioned the possibility of M. a. paratuberculosis (MAP)?
MAP & CROHN'S & REDHILL BIOPHARMA - MORE DETAILS.
2018-08-27 14:04:40 This news item provides a copy of a press release from RedHill BioPharma that gives more details about their clinical trial findings. Key findings:
This news item provides a copy of a press release from RedHill BioPharma that gives more details about their clinical trial findings. Key findings:
Primary endpoint successfully achieved - superior remission rate at week 26 in patients treated with RHB-104 (p= 0.013).
Key secondary endpoints also met, demonstrating consistent benefit to Crohn’s disease patients treated with RHB-104.
Comment: The real proof is in the final peer reviewed publication: Repeating comments from the prior new item, if the final published results of this trial are consistent with the claims in this press release, it represents a final piece of evidence indicating that MAP is a cause of Crohn’s disease. This would heighten the need for veterinary medicine, animal agriculture, and relevant governmental agencies concerned with food safety to limit contamination of food and water by MAP.
WELCOME
2018-08-18 17:02:32Welcome to the updated and improved johnes.org!!
Thanks to the support from our generous sponsors, our website has a fresh look, more images, and 100% edited and updated content. We give special thanks to our platinum sponsors, Zoetis and encourage you to follow links to their home pages.
If you are on our e-list, you will continue to receive notification of updates and news items. If you wish your name to be added to our e-list, click the "subscribe" button in the footer.
« Previous 1 … 16 17 18