Marco Roller and six colleagues in Germany and Brazil have published an excellent review article on MAP infections in zoo animals. This Open Access article appears in Frontiers in Veterinary Science (19 pages; 171 references).
ABSTRACT
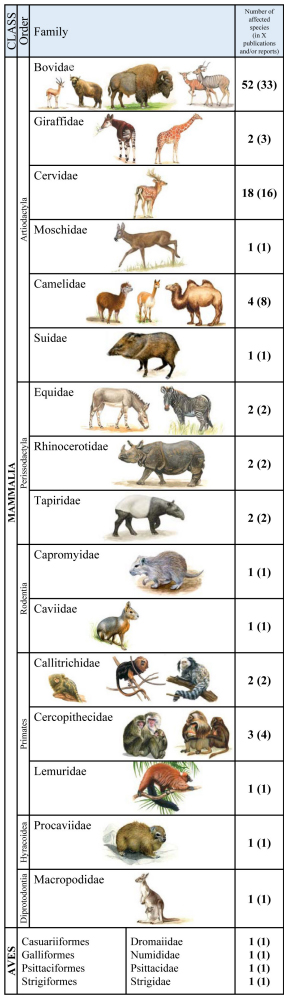 Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) is the causative agent of paratuberculosis (ParaTB or Johne’s disease), a contagious, chronic and typically fatal enteric disease of domestic and non-domestic ruminants. Clinically affected animals present wasting and emaciation. However, MAP can also infect non-ruminant animal species with less specific signs. Zoological gardens harbor various populations of diverse animal species, which are managed on limited space at higher than natural densities. Hence, they are predisposed to endemic trans-species pathogen distribution. Information about the incidence and prevalence of MAP infections in zoological gardens and the resulting potential threat to exotic and endangered species are rare. Due to unclear pathogenesis, chronicity of disease as well as the unknown cross-species accuracy of diagnostic tests, diagnosis and surveillance of MAP and ParaTB is challenging. Differentiation between uninfected shedders of ingested bacteria; subclinically infected individuals; and preclinically diseased animals, which may subsequently develop clinical signs after long incubation periods, is crucial for the interpretation of positive test results in animals and the resulting consequences in their management. This review summarizes published data from the current literature on occurrence of MAP infection and disease in susceptible and affected zoo animal species as well as the applied diagnostic methods and measures. Clinical signs indicative for ParaTB, pathological findings and reports on detection, transmission and epidemiology in zoo animals are included. Furthermore, case reports were re-evaluated for incorporation into accepted consistent terminologies and case definitions.
Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) is the causative agent of paratuberculosis (ParaTB or Johne’s disease), a contagious, chronic and typically fatal enteric disease of domestic and non-domestic ruminants. Clinically affected animals present wasting and emaciation. However, MAP can also infect non-ruminant animal species with less specific signs. Zoological gardens harbor various populations of diverse animal species, which are managed on limited space at higher than natural densities. Hence, they are predisposed to endemic trans-species pathogen distribution. Information about the incidence and prevalence of MAP infections in zoological gardens and the resulting potential threat to exotic and endangered species are rare. Due to unclear pathogenesis, chronicity of disease as well as the unknown cross-species accuracy of diagnostic tests, diagnosis and surveillance of MAP and ParaTB is challenging. Differentiation between uninfected shedders of ingested bacteria; subclinically infected individuals; and preclinically diseased animals, which may subsequently develop clinical signs after long incubation periods, is crucial for the interpretation of positive test results in animals and the resulting consequences in their management. This review summarizes published data from the current literature on occurrence of MAP infection and disease in susceptible and affected zoo animal species as well as the applied diagnostic methods and measures. Clinical signs indicative for ParaTB, pathological findings and reports on detection, transmission and epidemiology in zoo animals are included. Furthermore, case reports were re-evaluated for incorporation into accepted consistent terminologies and case definitions.
COMMENT
At least half of zoos in North America have had animals diagnosed with Johne’s disease. The infection spreads among institutions by the trade of animals; a practice that is essential for captive breeding programs. This led to a meeting of major zoo veterinarians and other zoo staff at the White Oak Conservation Center in Yulee, Florida in 1998. The 17-page proceedings of that meeting laid the groundwork for the control and prevention of Johne’s disease in zoological institutions. The White Oak proceedings are frequently cited in this publication by Rollo et al. Because these proceedings are hard to access, I have made it available here and on the website page about MAP infections of zoo ruminants.